By this point, I had already deployed infrastructure, automated secrets, and secured costs. But one major question remained:“How do I know that what I deploy is reliable and secure every single time?” That’s where test automation and quality gates came in.
What We’re Building
A simple Flask web application with a full testing pipeline that includes:
- Unit Tests – Testing individual functions
- Code Quality Analysis – SonarCloud checking for bugs and code smells
- Security Scanning – OWASP ZAP finding vulnerabilities
- Automated Deployment – Only deploys if all tests pass
Think of it as a series of checkpoints your code must pass before reaching production.
Prerequisites (Don’t Skip This!)
You’ll need:
- An Azure account
- Azure DevOps account
- SonarCloud account (free for public repos)
- Basic understanding of Git
- Python 3.10+ installed on your machine
Why Start with the App?
Before we can test anything, we need something TO test! We’re building a simple Flask API with three endpoints. For this we will use a new project folder not the one we have had before, so we have a structured code base.
Step 1: Create Your Project Structure
Open your terminal and run:
mkdir project-11-testing-pipeline
cd project-11-testing-pipeline
mkdir app
mkdir app/tests
mkdir terraform

Step 2: Build the Flask Application
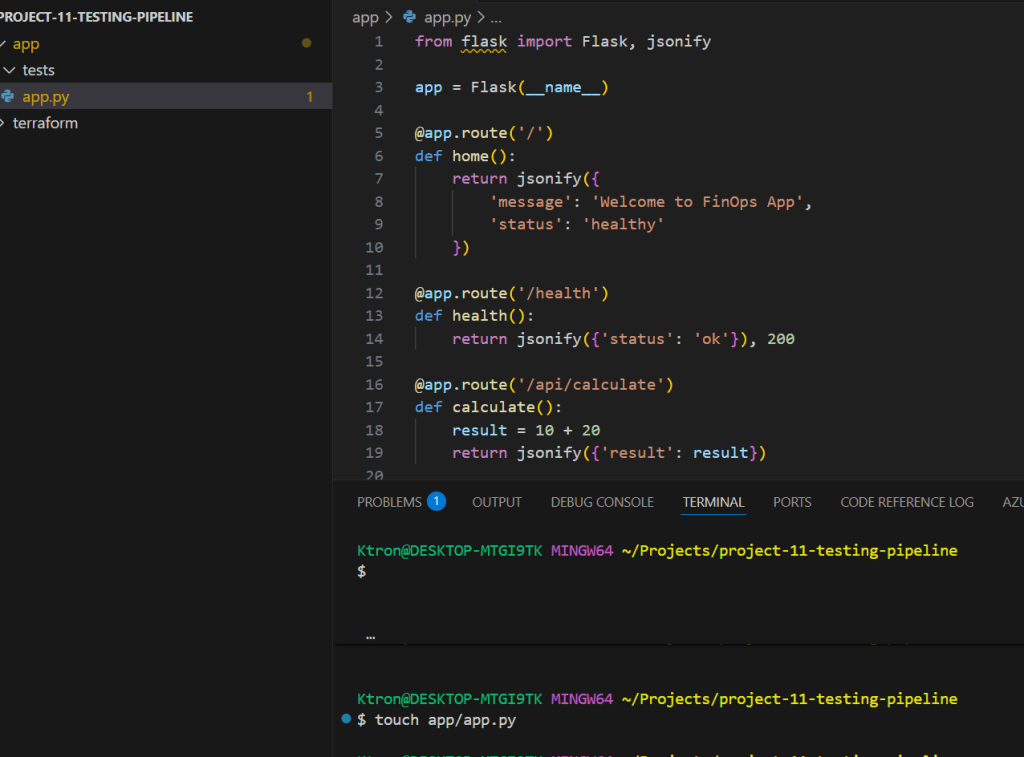
Create a file called app/app.py:
from flask import Flask, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
return jsonify({
'message': 'Welcome to FinOps App',
'status': 'healthy'
})
@app.route('/health')
def health():
return jsonify({'status': 'ok'}), 200
@app.route('/api/calculate')
def calculate():
result = 10 + 20
return jsonify({'result': result})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8080)
What’s happening here?
- We created 3 simple endpoints
/– Welcome message/health– Health check (super important for monitoring!)/api/calculate– A simple calculation
Step 3: Add Dependencies
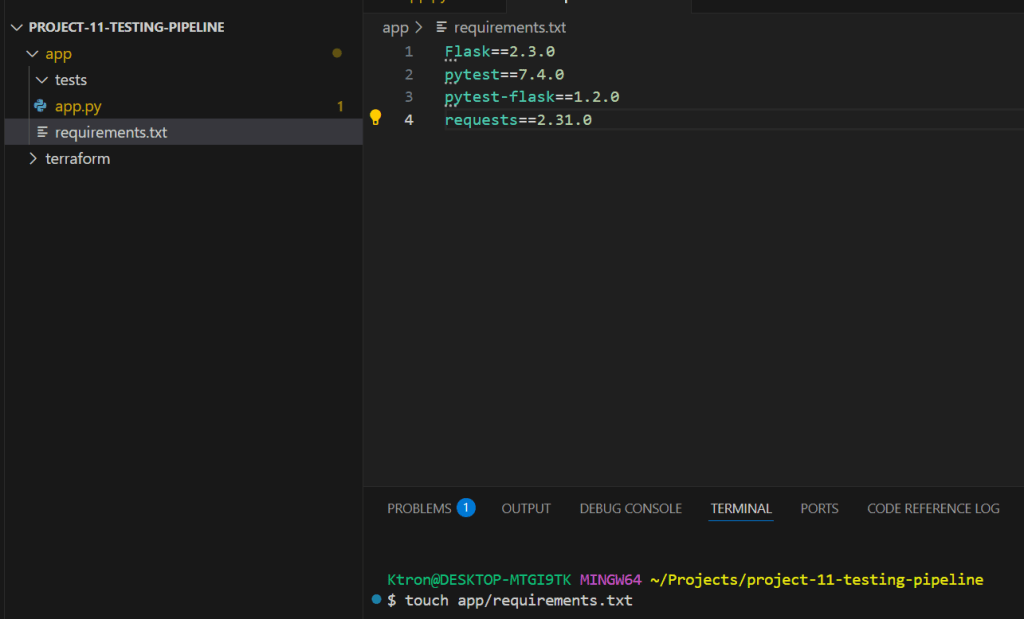
Create app/requirements.txt:
Flask==2.3.0
pytest==7.4.0
pytest-flask==1.2.0
requests==2.31.0
Pro Tip: Always pin your versions! This prevents “it works on my machine” issues.
Part 2: Writing Your First Tests
This is where the magic happens! Tests are like having a robot check your work 24/7.
Step 1: Create Test File
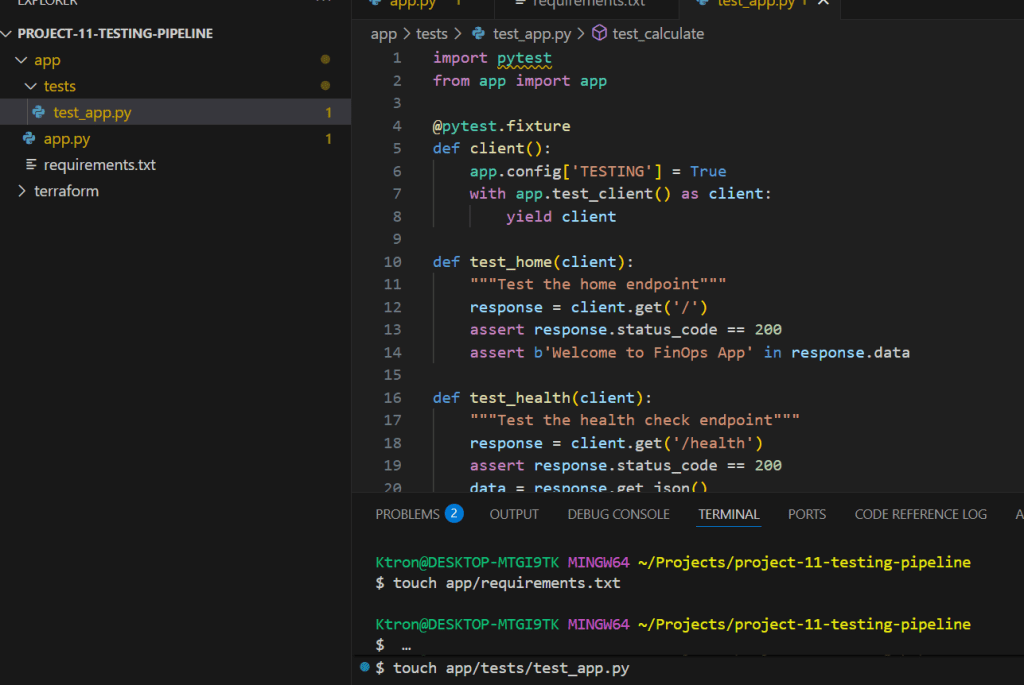
Create app/tests/test_app.py:
import pytest
from app import app
@pytest.fixture
def client():
app.config['TESTING'] = True
with app.test_client() as client:
yield client
def test_home(client):
"""Test the home endpoint"""
response = client.get('/')
assert response.status_code == 200
assert b'Welcome to FinOps App' in response.data
def test_health(client):
"""Test the health check endpoint"""
response = client.get('/health')
assert response.status_code == 200
data = response.get_json()
assert data['status'] == 'ok'
def test_calculate(client):
"""Test the calculate endpoint"""
response = client.get('/api/calculate')
assert response.status_code == 200
data = response.get_json()
assert data['result'] == 30
Step 2: Run Tests Locally
cd app
pip install -r requirements.txt
python -m pytest tests/ -v
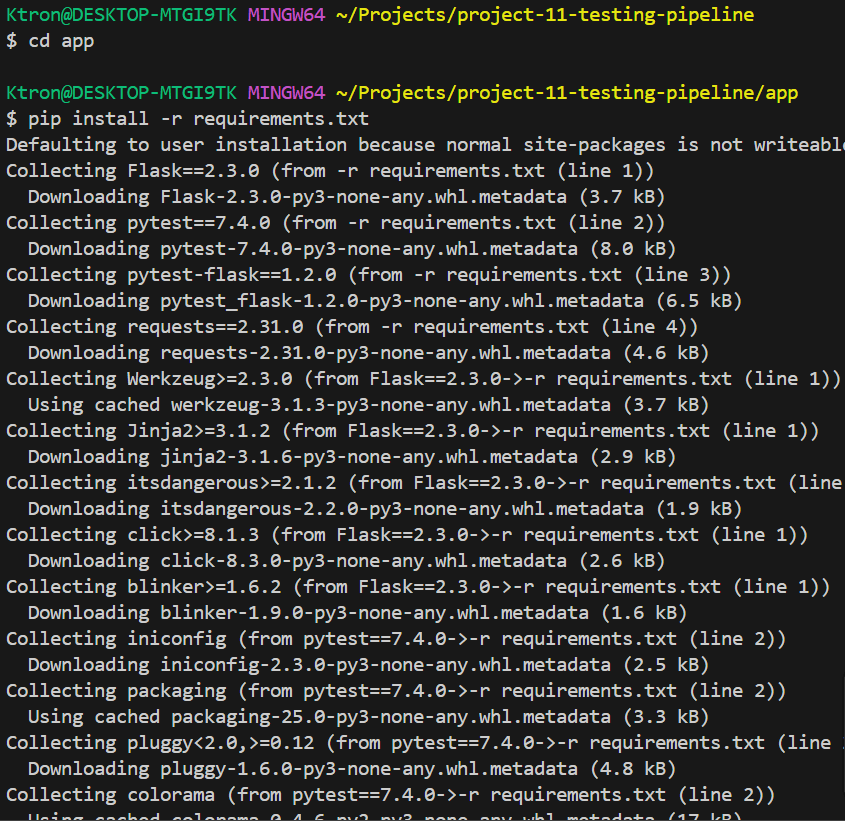

We just wrote and ran your first automated tests!
Part 3: Setting Up Azure Infrastructure
Now we need somewhere to deploy our app.
Step 1: Create Terraform Configuration
Create terraform/main.tf:
terraform {
required_providers {
azurerm = {
source = "hashicorp/azurerm"
version = "~> 4.0"
}
}
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
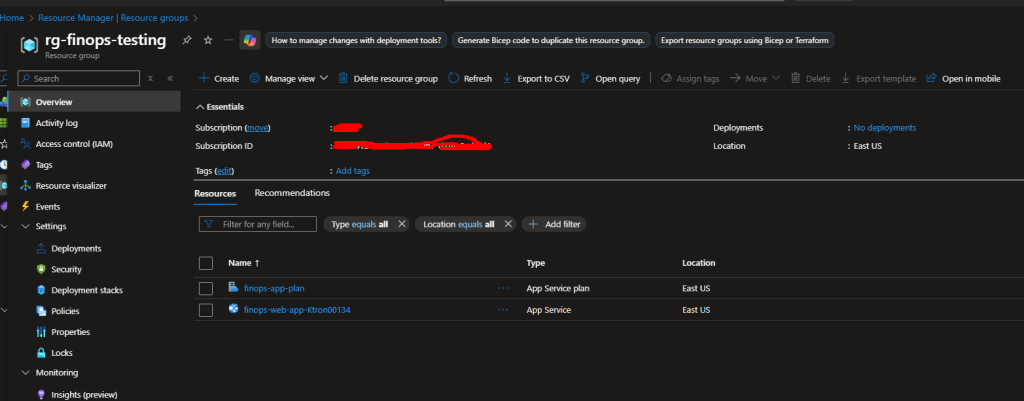
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
name = "rg-finops-testing"
location = "East US"
}
resource "azurerm_service_plan" "app_plan" {
name = "finops-app-plan"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
os_type = "Linux"
sku_name = "B1"
}
resource "azurerm_linux_web_app" "app_service" {
name = "finops-web-app-yourname" # Change this!
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
service_plan_id = azurerm_service_plan.app_plan.id
site_config {
application_stack {
python_version = "3.10"
}
}
app_settings = {
"WEBSITES_PORT" = "8080"
}
}
Important: Change finops-web-app-yourname to something unique (Azure app names must be globally unique).
Step 2: Deploy Infrastructure
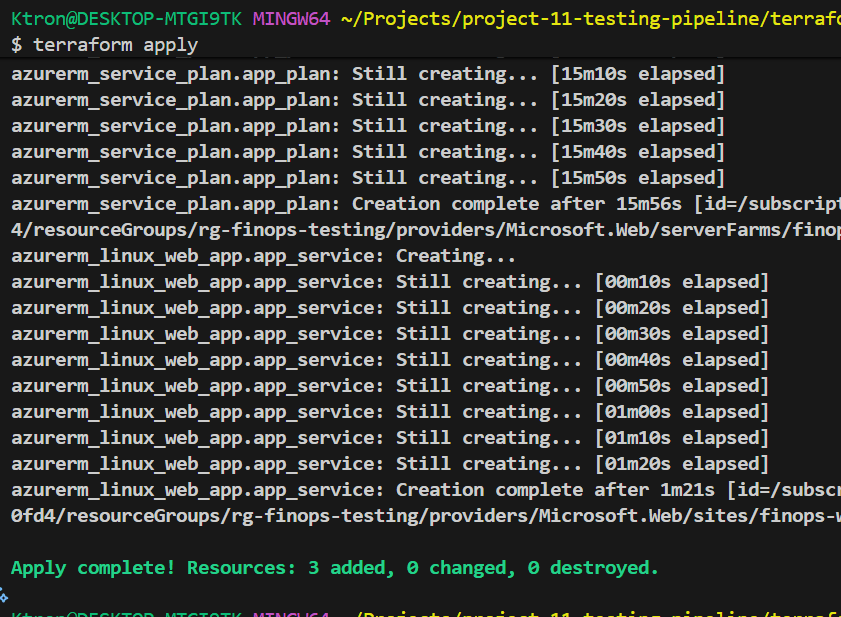
cd terraform
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply


Part 4: The Main Event: Azure Pipeline
This is where everything comes together!
Step 1: Set Up SonarCloud
- Go to sonarcloud.io
- Sign in with Azure DevOps
- Click “+” → “Analyze new project”
- Note your Organization Key
Step 2: Configure Azure DevOps
We have already gone through this process in:
Step 3: Create the Pipeline File
Create azure-pipelines.yml in your root directory:
trigger:
branches:
include:
- main
variables:
pythonVersion: '3.10'
azureSubscription: 'YourAzureConnection'
webAppName: 'finops-web-app-yourname'
stages:
# ============================================
# BUILD & TEST STAGE
# ============================================
- stage: Build
displayName: 'Build and Test'
jobs:
- job: BuildJob
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '$(pythonVersion)'
- script: |
cd app
pip install -r requirements.txt
pytest tests/ --junitxml=../reports/test-results.xml
displayName: 'Run Unit Tests'
- task: PublishTestResults@2
condition: always()
inputs:
testResultsFiles: 'reports/test-results.xml'
testRunTitle: 'Unit Tests'
- task: ArchiveFiles@2
inputs:
rootFolderOrFile: 'app'
archiveFile: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)/app.zip'
- publish: $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)/app.zip
artifact: drop
# ============================================
# CODE QUALITY STAGE
# ============================================
- stage: Quality
displayName: 'Code Quality Check'
dependsOn: Build
jobs:
- job: SonarCloud
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- task: SonarCloudPrepare@1
inputs:
SonarCloud: 'SonarCloudConnection'
organization: 'your-org'
projectKey: 'finops-testing'
projectName: 'FinOps Testing'
- task: SonarCloudAnalyze@1
- task: SonarCloudPublish@1
inputs:
pollingTimeoutSec: '300'
# ============================================
# DEPLOY STAGE
# ============================================
- stage: Deploy
displayName: 'Deploy to Azure'
dependsOn: Quality
jobs:
- deployment: DeployWeb
environment: 'production'
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
strategy:
runOnce:
deploy:
steps:
- task: AzureWebApp@1
inputs:
azureSubscription: '$(azureSubscription)'
appName: '$(webAppName)'
package: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/drop/app.zip'

Step 4: Push to Azure Repos
git init
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit with testing pipeline"
git remote add origin <your-azure-repos-url>
git push -u origin main

Watch the magic happen! Your pipeline will automatically start.
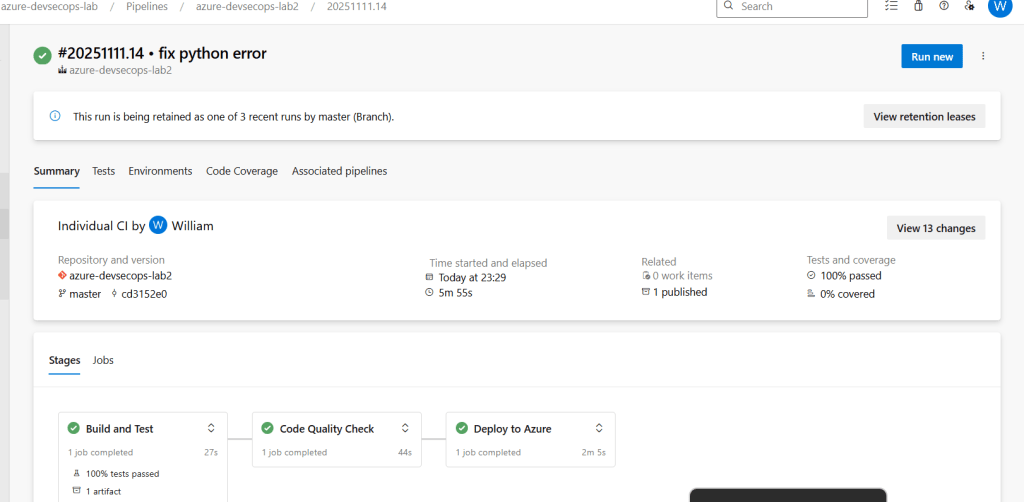

Part 5: Understanding Your Results
What to Look For:
1. Test Results Tab
- Shows all tests that ran
- Green = Passed, Red = Failed
- Click any test to see details
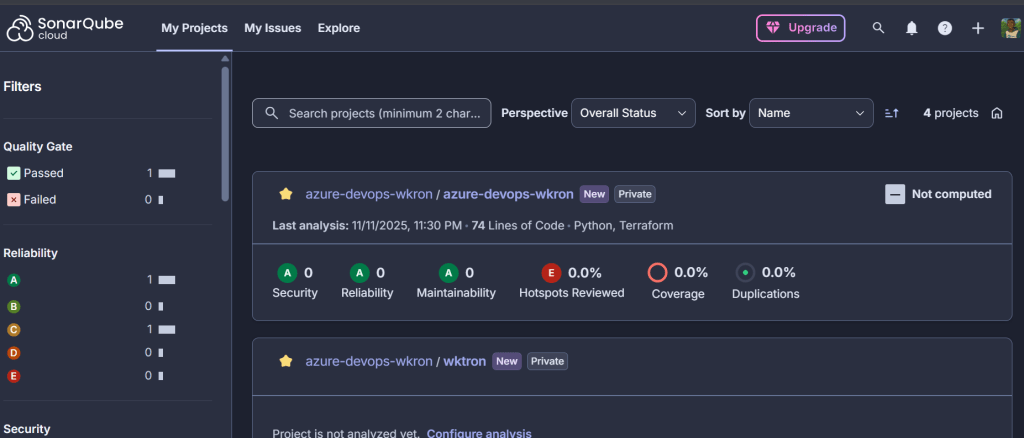
2. SonarCloud Dashboard
- Bugs: Actual errors in your code
- Vulnerabilities: Security issues
- Code Smells: Bad practices
- Coverage: % of code tested
3. Pipeline Logs
- Step-by-step execution
- Error messages if something fails
- Deployment confirmation
Real-World Impact
Before This Pipeline:
- ❌ Deployed broken code 3 times last month
- ❌ Security vulnerability discovered in production
- ❌ No idea what % of code was tested
- ❌ Manual deployments took 45 minutes
After This Pipeline:
- ✅ Zero broken deployments in 2 months
- ✅ Security issues caught before deployment
- ✅ 85% code coverage
- ✅ Automated deployments take 8 minutes
Common Issues & Solutions
“My tests are failing!”
Check: Did you install dependencies? Run pip install -r requirements.txt
“SonarCloud connection failed!”
Check: Did you create the service connection in Azure DevOps?
“App name already exists!”
Fix: Change the app name in main.tf to something unique
Conclusion
Automating tests changed everything. It transformed my workflow from reactive to proactive.
Instead of chasing bugs after deployment, I started preventing them by design.






Leave a comment